Deploy hooks
Trigger a deployment of an app via a HTTP request.
How it works
Deploy hooks are unique URLs which can be used to trigger a new deployment for an app. They can be used in CI flows to automatically release new versions of the app.
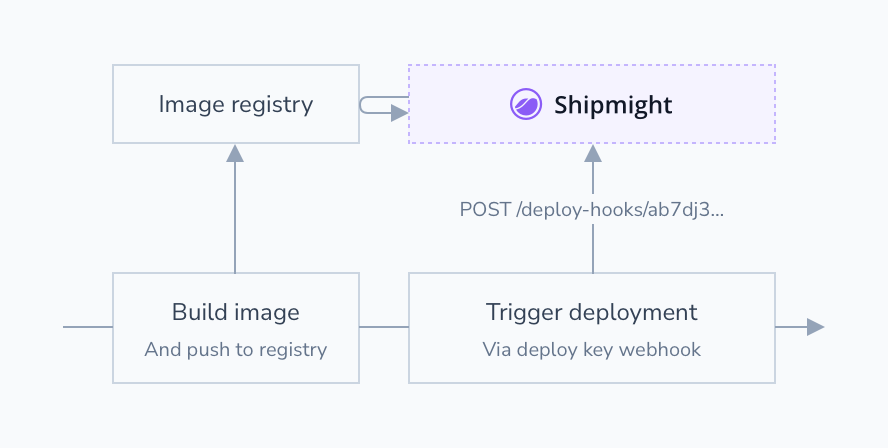
Triggering a deployment via a deploy hook achieves the same as making a manual deployment via the UI.
Example GitHub workflow
Here's a sample GitHub workflow which implements this flow by pushing an image to GitHub Container Registry and triggering a new deployment:
name: Deploy
on:
- push
jobs:
image:
runs-on: ubuntu-latest
steps:
- uses: actions/checkout@v2
- name: Store commit ref
run: echo "SHORT_SHA=`git rev-parse --short HEAD`" >> $GITHUB_ENV
- name: Build and push image
run: |
docker build -t ghcr.io/<username>/<imageName>:${{ env.SHORT_SHA }} .
echo ${{ secrets.GITHUB_TOKEN }} | docker login ghcr.io -u <username> --password-stdin
docker push ghcr.io/<username>/<imageName>:${{ env.SHORT_SHA }}
- name: Trigger deployment
run: |
curl \
-X POST \
-H 'Content-Type: application/json' \
-H 'X-Deploy-Hook-Token: ${{ secrets.DEPLOY_HOOK }}' \
--data '{"imageTag":"${{ env.SHORT_SHA }}"}' \
https://<shipmight-url>/api/v1/dh
Creating deploy hooks
You can find deploy hooks under your application or job settings:
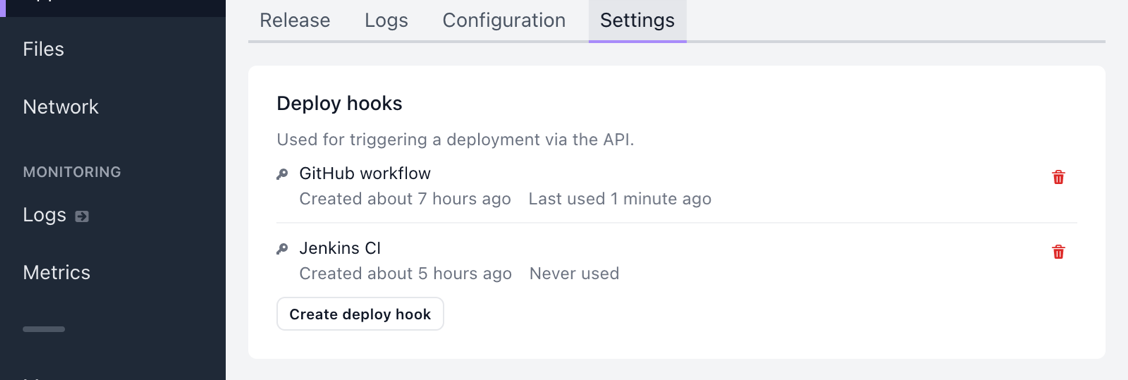
Selecting Create deploy hook opens a modal where you’ll be able to select:
- Name
Descriptive name for the hook. Used for presentational purposes only. It’s recommended to include information about where and by whom this hook is used. Cannot be changed later.
After creating the key you’ll be able to copy the unique hook token which is used in the HTTP request URL. This is the only time you can copy this token. If you lose it, you can simply create a new hook and delete the old one.
Deleting a deploy hook invalidates it immediately, so any further requests to it begin failing.
Trigger a deployment via a HTTP request
The endpoint URL is:
POST /api/v1/dh
Request headers must contain the hook token:
X-Deploy-Hook-Token: <deploy-hook-token>
Request body must contain the new image tag to deploy:
{
"imageTag": "<tag>"
}
Examples
Example curl request for an application:
curl \
-X POST \
-H 'Content-Type: application/json' \
-H 'X-Deploy-Hook-Token: <deploy-hook-token>' \
--data '{"imageTag":"1.2.0"}' \
https://<shipmight-url>/api/v1/dh
Example curl request for a job:
curl \
-X POST \
-H 'Content-Type: application/json' \
-H 'X-Deploy-Hook-Token: <deploy-hook-token>' \
--data '{"instanceEnvironmentVariables":[{"name":"EXAMPLE_VAR","value":"example"}]}' \
https://<shipmight-url>/api/v1/dh
Response status codes
The following status codes are supported:
201Deployment was triggered successfully400Malformed request or validation error404Deploy hook was not found500Unknown error happened